Create Your First Project
Start adding your projects to your portfolio. Click on "Manage Projects" to get started
Extensibility Portal Inside
A central console that allows enterprise admins to extend and customize their respective subscribed applications independently without extensive support. The intention has been to make this Customer-centric which tailors deployment approaches that prioritize their unique needs and preferences.
Context
Procurement customers seek a scalable product that promptly addresses their business needs, taking into account the following considerations:
-
Customize the application with minimal-to-zero dependency on the Service Provider.
-
Accelerate time-to-Market of functional features to support evolving business requirements
-
User-friendly interface to manage extensions and configurations.
-
Application enriched with intelligent capabilities to:-
-
Provide guidance throughout the user journey.
-
Propose and recommend solutions for business cases.
-
Prevent human errors.
-
-
Comprehensive end-to-end functionality, streamlining processes and minimizing reliance on external Service Provider interactions
-
Address industry-specific challenges effectively.
-
Full automation of the metadata process : (Configure → Test → Deploy)
-
Versioned (created by Key User) :
-
Monitor and Manage changes.
-
Maintain a comprehensive long-term change history.
-
Detailed and concise release notes for all implemented features.
-
Goal
Extensibility is a basic expectation of customers looking to customize/scale the out-of-the-box product for their business needs.
This service provides a cross-application layer that helps with the following:
-
Enable the customers to add customizations at the field/UI/Workflow levels with no code changes.
-
Use the power of AI to suggest best practices and guide the customers through the changes.
-
Consistency between various SAP applications in the lifecycle of customizations.
-
Version and track changes, ability to rollback updates, promote changes from Test to Prod.
Process
For the project, we used the following process:
1. Requirements Refinement
2. User Flow and Architecture
3. Iteration and Prototypes
4. User Testing and Validation
5. Refinement and Future Scope
My Role
As the Lead Designer on this project, I am responsible for crafting a seamless user experience that empowers customers to customize and scale SAP applications without requiring code changes.
My role involves:
-
User-Centered Design: Collaborating with cross-functional teams to understand customer needs and pain points, ensuring the design aligns with their business objectives.
-
AI-Driven Guidance: Designing intuitive workflows that leverage AI to suggest best practices and guide users effectively through customization processes.
-
Consistency Across Applications: Ensuring a unified design language and interaction consistency across various SAP applications for managing customizations.
-
Version Control & Tracking: Creating clear, user-friendly interfaces for tracking changes, managing versions, and promoting updates from test environments to production.
-
Prototyping & Validation: Developing high-fidelity prototypes and conducting usability testing to refine designs based on user feedback.
Requirements Refinement
The Product Manager presents a curated list of requirements and proposed features aligned with the objectives for the upcoming release, specifically focusing on onboarding plans. These initial requirements are then meticulously analyzed and refined to gain a deeper understanding of the user problems we aim to address.
For the current onboarding plans, the outlined requirements were further elaborated through collaborative discussions with the triad—Product Management, Engineering, and UX—to ensure alignment and clarity in problem-solving.

User Flow and Architecture
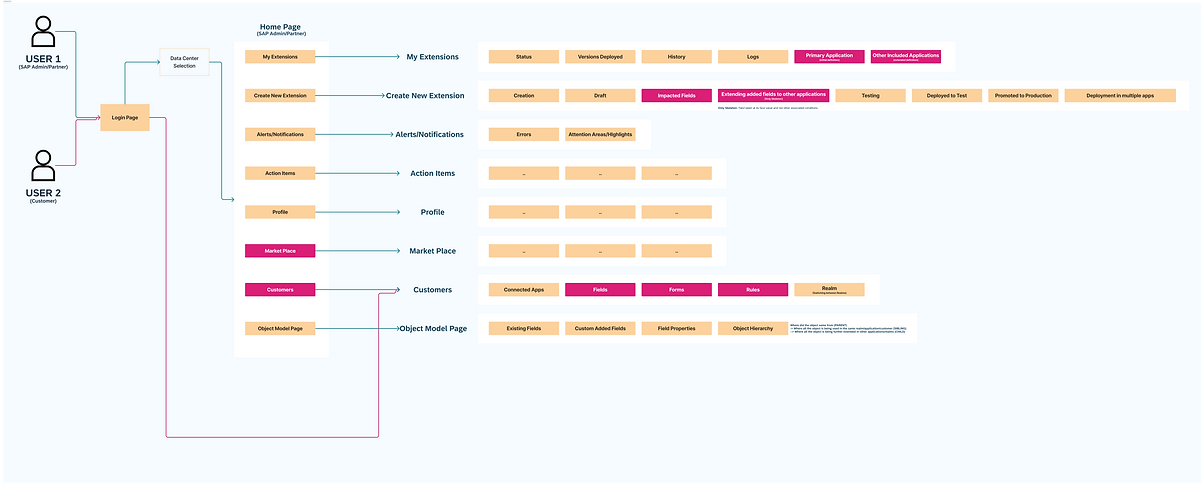
1. Entry Point: Extensibility Portal
-
Login/Authentication:
-
User logs into the extensibility portal via SSO or tenant-specific credentials.
-
User is greeted with a dashboard showcasing key stats (active extensions, pending updates, etc.).
-
2. Dashboard Overview
-
Options Available:
-
View and manage existing extensions.
-
Create a new extension.
-
Onboard applications to the portal.
-
Manage custom fields.
-
3. Manage Existing Extensions
Task Flow:
-
User clicks on "Manage Extensions."
-
A table/grid displays the list of extensions with details like deployment status, version history, and logs.
-
Actions Available:
-
View Logs: Inspect change history and logs for specific extensions.
-
Rollback Update: Select a previous version to roll back to if needed.
-
Promote to Production: Approve and deploy changes from test to production.
-
4. Create New Extension
Task Flow:
-
User selects "Create New Extension."
-
Step 1: Define Scope
-
Select application(s) and tenant.
-
Choose customization type: Field/UI/Workflow.
-
-
Step 2: Configure Extension
-
Add custom fields, UI elements, or workflows.
-
Utilize a drag-and-drop editor for ease.
-
Input validation ensures changes adhere to system constraints.
-
-
Step 3: AI Recommendations
-
AI suggests best practices based on input.
-
User reviews and accepts/rejects recommendations.
-
-
Step 4: Preview & Validate
-
User previews changes within a simulated environment.
-
-
Step 5: Save & Test
-
Save the extension for testing.
-
Iteration and Prototypes
Over several weeks, I conducted multiple iterations of workflows for the feature, collaborating closely with stakeholders to assess feasibility and gather feedback for improvements. This iterative process involved regular peer-review sessions and presenting the vision at bi-weekly Design Sharing sessions, which bring together various stakeholders and users to provide feedback on upcoming features.
Here are a few snippets of the iterations and feedback received in the sessions.
Initial Approach:
Over several weeks, I conducted multiple iterations of workflows for the feature, collaborating closely with stakeholders to assess feasibility and gather feedback for improvements. This iterative process involved regular peer-review sessions and presenting the vision at bi-weekly Design Sharing sessions, which bring together various stakeholders and users to provide feedback on upcoming features.
Here are a few snippets of the iterations and feedback received in the sessions.

Initial Feedback and Synthesis:
We took a look on initial iterations and gathered insights from users and stakeholders to identify pain points, validate assumptions, and refine workflows. This collaborative process ensured the designs are aligned with user needs while addressing feasibility constraints.

Revised Definition and Flow:


Key Screens:
-
Project Home Page: This screen features a clear, card-based layout for managing projects, with tabbed navigation, color-coded status labels, and key project details. A search bar and filters enhance usability, while functional icons offer quick actions. The design emphasizes clarity, organization, and efficiency, ensuring a seamless user experience for project management.

-
Extension Detail and Revision feature pages: These screens feature a structured, three-panel layout that organizes entities, fields, and detailed information efficiently. Key highlights include collapsible navigation, editable fields, and action buttons for revisions. The right panel provides contextual information with adjustable settings, ensuring usability and clarity. The design prioritizes streamlined workflows and enhanced data management.

Future Work and Learnings
This project was a great eye opener not only for me as a designer but the whole team, where we realized what an admin user wanted to make their task easy and seamless while enhancing their experience. Below are some of the learnings which we realized and have thought of putting in future iterations.
1. Future Work: Enhancements and Features
-
User-Centered Improvements: Explore opportunities to enhance usability, such as improved navigation, better filtering options, and dynamic layouts for varied user needs.
-
AI-Powered Enhancements: Implement AI for predictive assistance, like suggesting frequently used entities or auto-completing fields based on context.
-
Personalization: Use AI to adapt the interface based on user behavior, providing a more tailored experience.
-
Real-Time Feedback: Add AI-driven tools for real-time error detection, validation, or optimization of input fields and workflows.
2. Learnings: Insights from the Current Design
-
Scalability: The structured layout supports scalability but could benefit from dynamic content prioritization driven by AI.
-
Consistency: Consistent use of labels, icons, and actions simplifies navigation, but introducing adaptive elements could improve responsiveness to diverse workflows.
-
Data Overload: Dense information in the current layout can overwhelm users. AI can analyze usage patterns to declutter and surface the most relevant data.
-
Efficiency Gaps: Identify bottlenecks in user interaction and address them with features like AI-based automation for repetitive tasks.
3. AI-First Approach: Strategic Integration
-
Proactive Recommendations: Use AI to recommend actions, corrections, or insights, such as suggesting related entities or predicting project statuses.
-
Voice and Conversational Interfaces: Incorporate natural language processing (NLP) for hands-free navigation and data input.
-
Learning and Optimization: Employ AI to track user behavior and continuously refine the design based on real-time analytics.
-
Accessibility: AI can improve accessibility through voice commands, real-time translations, and adaptive layouts for diverse user abilities.
4. Continuous Learning: Staying Ahead
-
Feedback Integration: Regularly collect user feedback and use AI to analyze trends and patterns for iterative improvements.
-
Keeping Abreast of AI Trends: Stay updated on advancements in AI technologies like generative AI, which can be leveraged for more dynamic and creative design solutions.
-
Experimentation: Test AI-driven features in controlled environments to identify effective solutions and avoid over-engineering.
This approach ensures that future developments not only address current limitations but also position the design as a forward-thinking solution in an AI-driven landscape.

